
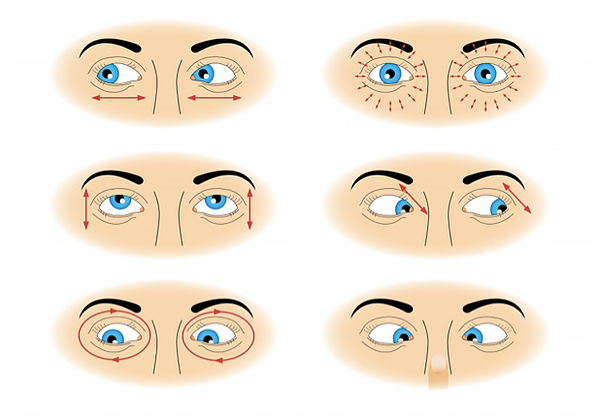
Procedure: To do this rotation, sit down in Padmasana with your head and spine erect and hands resting on your knees in yoga mudra. Lift the right fist with thumb
facing upwards. Keep your elbow straight while doing so. Focus your eyes on the thumb, keeping your head straight. Move your thumb clockwise with your gaze following
it. Repeat this five times and do the same anti-clockwise for another five times. Repeat the entire process by shifting your gaze towards the left thumb.
Benefits: Clockwise and Anti-clockwise rotations relax the eyes and safeguard them from any diseases and disorders. This exercise is ideal for those who spend long
hours in front of the computer.
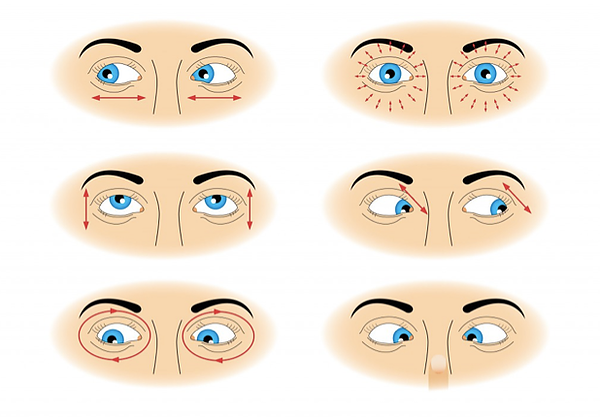
Procedure: To do sideway rotation, sit down in Padmasana keeping your head and back erect. Stretch your arms forward with your fists clasped and closed and thumbs
facing upwards, replicating the Linga mudra. Keep your gaze fixed on the thumbs. Bring the clasped fists closer to your eyes, placing them in between your eyebrows.
Move the fists to the right, with your eyeballs following the path. The head should remain straight while doing so. Bring the fists back to in between the eyebrows
with your eyes following back. Repeat the same on the left side. Repeat the entire procedure ten times, closing your eyes for 10 seconds after every
repetition.
Benefits: Side movement of eyeballs is good for people with myopia and hypermetropia.
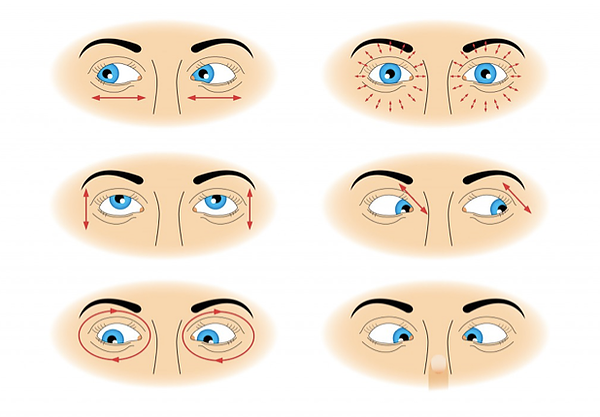
Procedure: To do the up and down eye rotation, sit on the floor with legs stretched out. Keep your back and head erect. Place both your hands on the respective
knees.Close your right fist and place it on your right knee with the thumb facing upwards. Keep your gaze fixed on any object in front of you. Now, breathe out deeply
and take your gaze upwards, keeping your head fixed. Breathe in and get back your gaze to the object. Do the same from lower gaze to upper gaze. Repeat the same
procedure with the left fist on your left thigh. Close your eyes for 15 seconds before repeating the exercise. Do the exercise 10 times.
Benefits: Constantly moving your eyes helps keep eye disorders at bay and improves vision.

Procedure: To do Palming, sit in a comfortable position. Rub your palms against each other, vigorously until you can feel the heat radiating from them. Place the palms
over your closed eyes and feel the warmth spreading.
Benefits: Palming is warming up your eyes for better circulation. It is a quick and easy way to relax your eyes. It improves blood circulation and keeps tiredness and
puffiness at bay.

Procedure: Sit down in Padmasana with your spine erect. Using your right thumb, close your right nostril. Inhale and exhale forcefully and quickly through your left
nostril. Do this about 20 times. You can feel your abdominal walls bellowing while doing the exercise. Make your last breath, long and profound. Now, repeat the same
process on your right nostril with the left thumb closing the left nostril. Finishing the exercise on both the nostrils makes for one bhastrika. Relax for about 30
seconds and repeat the entire process again. Do it for about 10 minutes.
Benefits: Bhastrika Pranayam boosts blood circulation to the head and improves vision. It also refreshes your physical and mental being.

Procedure: Sit down comfortably, either in Padmasana or Vajrasana. Place a candle at about two feet from where you are sitting. Light the candle and gaze at the flame
without blinking. You can count numbers in your head to keep track of time and for your mind to not waver. Look as long as you can. The longer you do, the
better.
Benefits: Trataka means to gaze at an object continuously for a fixed period. Doing so improves your concentration and vision. This eye exercise lowers high myopic eye
powers.

Procedure: Stand with your legs apart from each other and take a deep nasal inhalation. Bend your knees slightly.Bend your head slightly downwards and exhale through
your mouth.Make sure that the back is erect always, with your abdominal muscles in the relaxed position. Pull your navel up and inwards so that it comes closer to your
spine.Hold your breath for about 15 counts and then flap the abdominal muscles, forward and backward for 10 times with the breath under hold.
Benefits: Agnisara is a combination of two Sanskrit words – Agni (fire) and Sara (cleansing or washing). To be more precise, this exercise focuses on cleansing the
fire or Manipura chakra situated near the belly button.
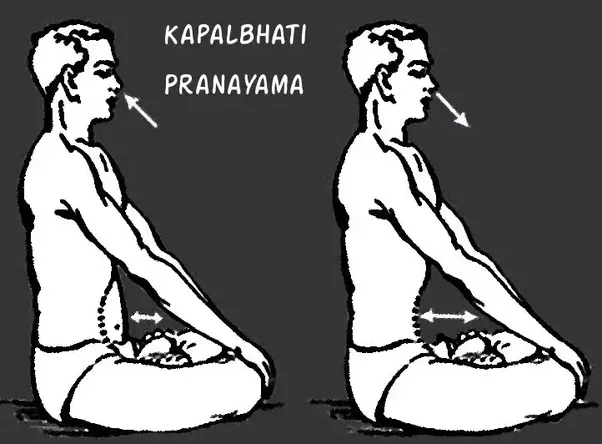
Procedure: Sit in a comfortable position. It could be Padmasana, Sukhasana, or Vajrasana. You can allow yourself to be supported by a wall, if you have back pain, as
this breathing exercise is a powerful one and beginners could find themselves subjected to back ache.Close your eyes and keep your hands in yoga mudra.Focusing on your
lower abdomen, make a quick inhalation followed by powerful and quick exhalations, [about 8 to 10 per inhale-exhale cycle for 1 to 2 seconds], to start with. A
beginner can keep her hand on the belly as she might find it difficult to concentrate during the initial repetitions.Increase the number of cycles slowly. With regular
practice, you can reach up to 100 counts.
Benefits: Cleanse your lungs and improve your circulation for a better vision with this skull shining breathing exercise. This is a very powerful exercise that ensures
you a flatter tummy, better vision, lustrous hair, and much more. The inhalation is almost nil while exhalations are powerful and in rapid succession.

Procedure: Sit comfortably in Sukhasana or Padmasana.Inhale deeply and empty your lungs with a forceful exhalation.Now, holding your breathing lock your chin with the
chest. This is known as the Jalandhar’s Bandha.Pull your belly inwards as much as possible so that it comes closer to your spine. This is known as the Udhiyana
Bandha.Now, hold the groin muscles upwards or hold yourself in Mooladhara bandha.Hold the Bandhas together for about 10 to 15 seconds to start with. Taking a deep
breath, release the Bandhas.Repeat for about 2 minutes, to begin with, increasing the time from 5 to 7 minutes.
Benefits: Along with being an excellent way to improve the circulation and cleanse the lungs, this also helps in easing disorders associated with reproductive organs.
Make sure that this pranayama is performed on an empty stomach.


Procedure: Sit comfortably in Sukhasana or Padmasana.Take a deep inhalation.As you exhale, chant Om as long as you can. The longer you can hold your breath, the better
the results are.One chanting completes one round. Relax with your eyes closed, breathing normally, for about 15 seconds before moving ahead with the next
repetition.Repeat this for 2 to 3 minutes, to begin with, increasing the duration to 10 minutes gradually.
Benefits: This is basically a meditation exercise, wherein you are expected to chant “OM”. This is ideal for those who want to relax. Kids can practice this to boost
their memory power. This breathing exercise involves inhalation and exhalation of longer duration.
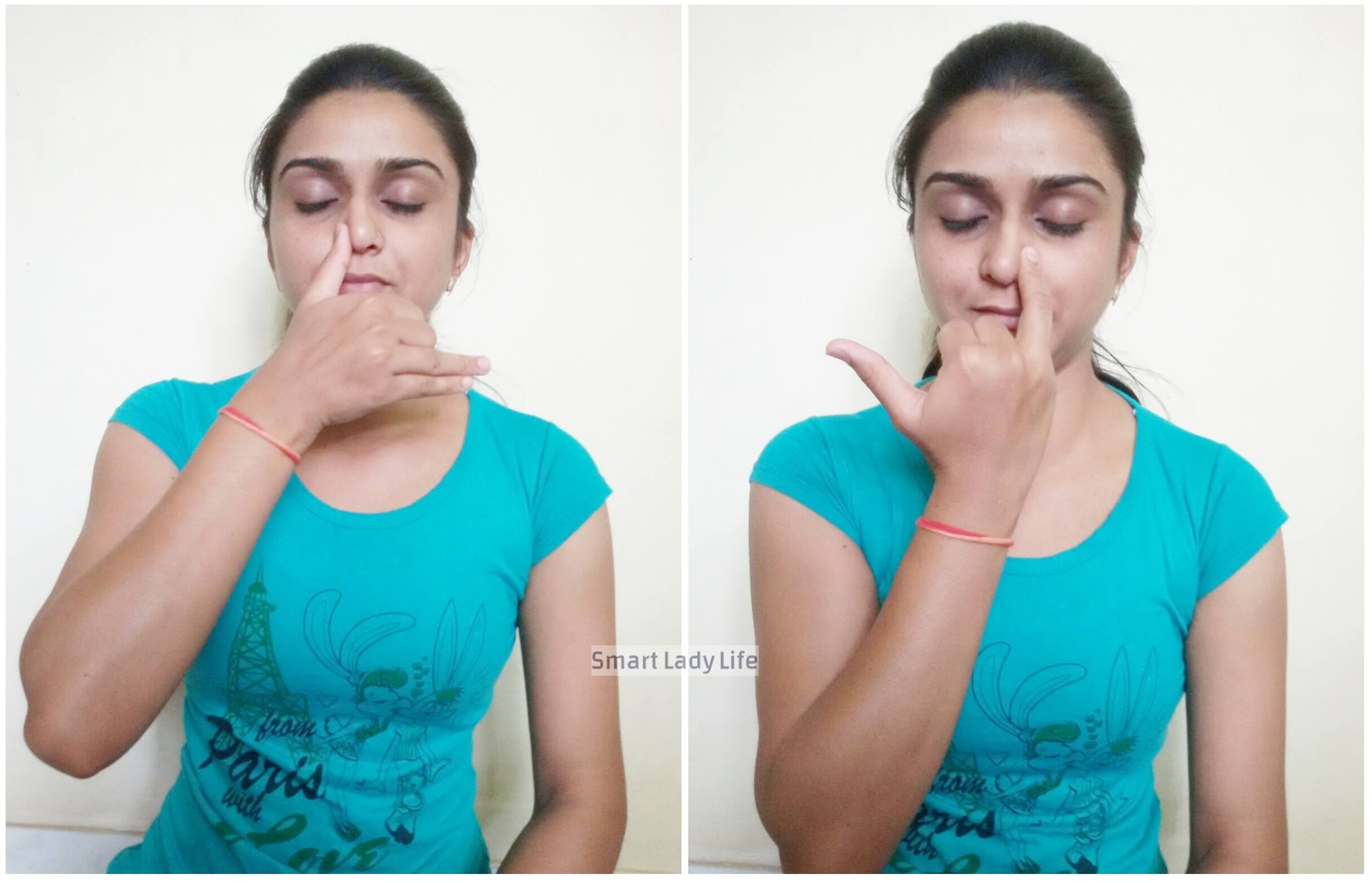

Procedure: Sitting in Padmasana or Sukhasana, stretch out your hands, resting the palms on your knees in yoga mudra.Lift your right hand in Pranayama mudra.Using the
thumb, close the right nostril.Take a deep inhalation with the left nostril.Closing the left nostril, allow exhalation through the right nostril.Now, inhale through
the right nostril and allow exhalation via left nostril.This completes one round of Anuloma – Viloma Pranayama.Repeat for 10 to 15 times to start with, increasing to
50 to 75 times, gradually.
Benefits: This is the easiest of the pranayamas and is also known as the alternate nostril breathing exercise.
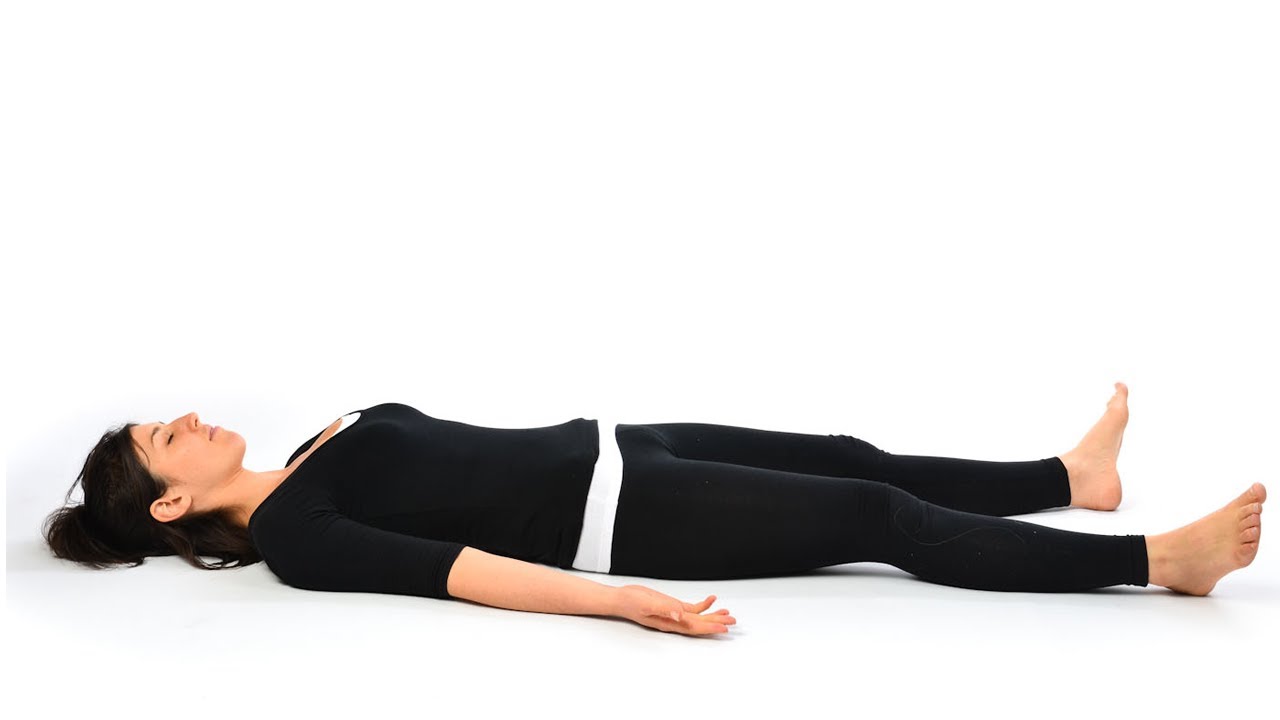

Procedure: Lie down in supine position.Keep your feet together or stretched out, as per your comfort level. Allow your hands to rest on either side of the body, palms
facing the ground. Close your eyes. Inhale and exhale deeply, allowing your body to relax completely.
Benefits: You should allow your body to relax after any workout session and the Corpse Pose is the ideal asana.

We provide yoga services in all life style disorders and wellbeing
Heart conditions that include diseased vessels, structural problems and blood clots.
Read More
Diabetes - A group of diseases that result in too much sugar in the blood (high blood glucose).
Read More
Obesity - A disorder involving excessive body fat that increases the risk of health problems.
Read More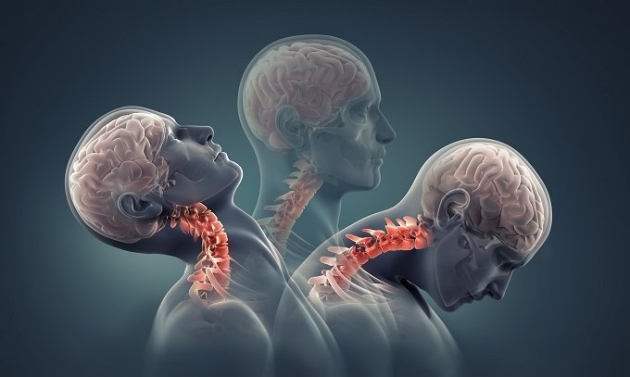
Cervical spondylosis is a common, age-related condition that affects the joints and discs in your cervical spine, which is in your neck.
Read More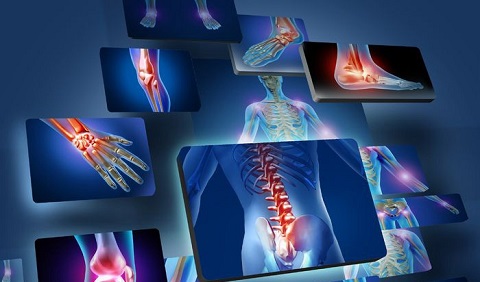
Arthritis - Inflammation of one or more joints, causing pain and stiffness that can worsen with age.
Read More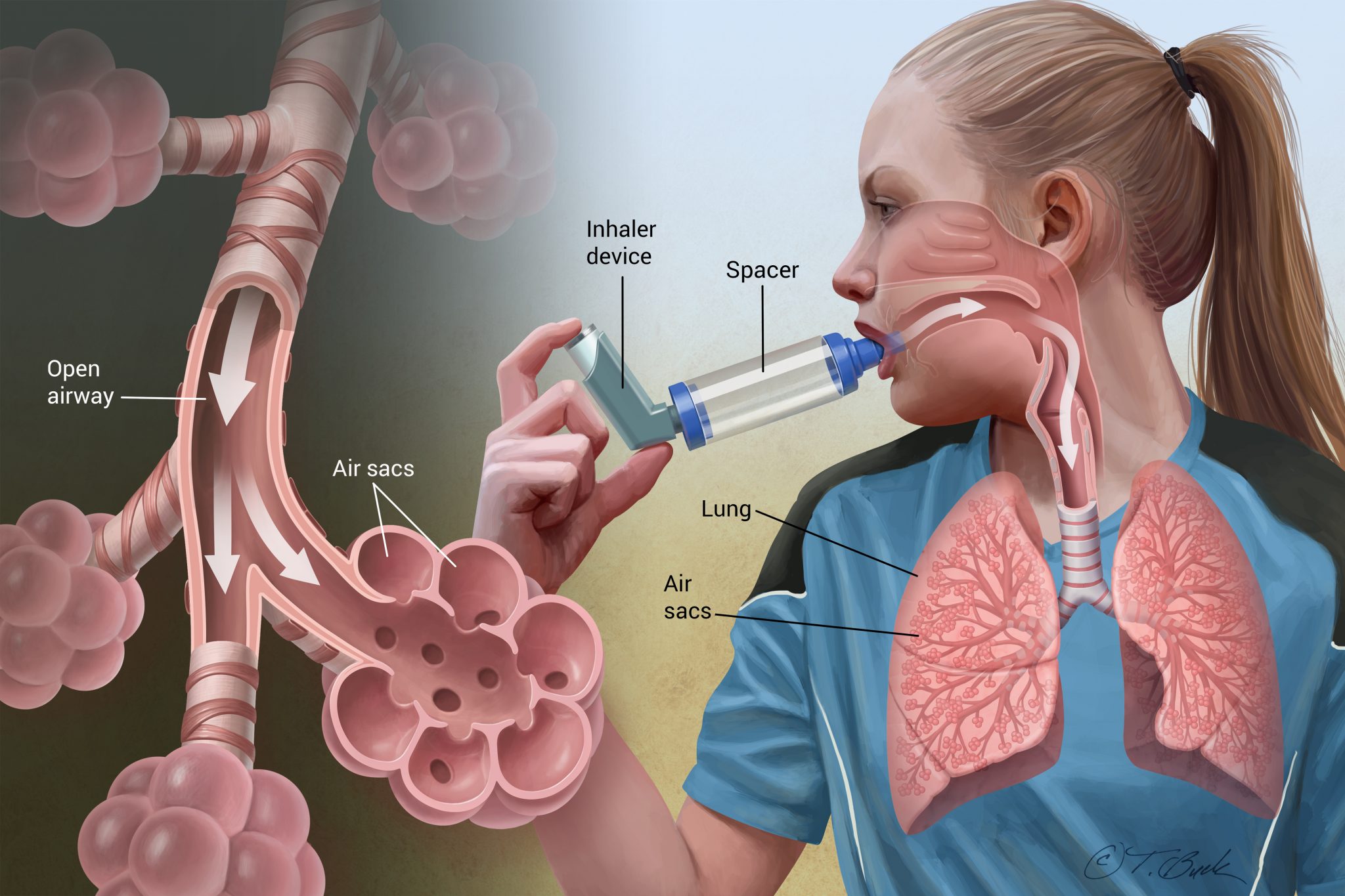
Asthma - A condition in which a person's airways become inflamed, narrow and swell and produce extra mucus, which makes it difficult to breathe.
Read More
A mental health disorder characterised by feelings of worry, anxiety or fear that are strong enough to interfere with one's daily activities.
Read More
PCOS - A hormonal disorder causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts on the outer edges.
Read More
Thyroid - Thyroid disease is a common problem that can cause symptoms because of over- or under-function of the thyroid gland.
Read More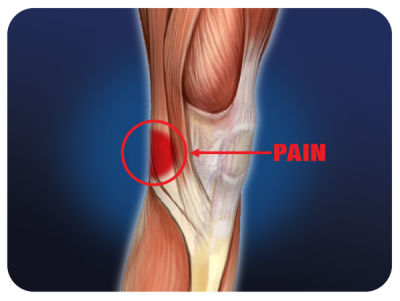
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative process that causes knee joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Read More
Migraine - A headache of varying intensity, often accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light and sound.
Read More
Gastric problems are usually more common in diabetics who have had the condition for longer, and is mostly caused by neuropathy affecting certain nerves in the digestive system.
Read More
Eye diseases like macular degeneration, glaucoma, and cataracts, can cause vision problems.
Read More
Shoulder problems happen when the soft tissues in the shoulder break down.
Read More
Yoga is for all age groups kids, children, tenage, young and adults.
Read More
Hair Loss - Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body.
Read More
Yoga helps to increase your height by opening your ligamnets, stiffed tendons, ball and socket joints.
Read More
Pranayama, breathing exercises, headstand, and fish pose are primarily the best for glowing skin.
Read More
Body Toning - Tone up you body curves and lose weight by yoga asanas.
Read More
General Fitness by yoga includes physical, mental and spiritual wellbeing.
Read More