
Bacteria, viruses, and parasites ingested through contaminated foods can enter the human body, resulting in foodborne illnesses. Toxins and certain fungi also can cause foodborne illnesses when accidentally ingested, while other chemical and physical hazards, such as cleaning solutions and small pieces of broken glass, can cause serious injury as well. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that approximately one in every six Americans (roughly 48 million people) experiences a foodborne illness each year. Of that number, the CDC says 128,000 require hospitalization and 3,000 die.3 Infants and young children, pregnant women, the elderly, and people with compromised immune systems particularly are vulnerable to contracting foodborne illnesses.
The microorganisms were found on kitchen equipment and tools that come in regular contact with potentially hazardous foods including meat, poultry, and seafood.
• Refrigerator drawers: If possible, remove the drawer from the refrigerator. Then, remove all the food inside and wash the bin thoroughly with a clean sponge or cloth
and mild dish detergent mixed with warm water. Rinse the bin with tap water and dry it. If the drawer has an odor, wash with 1 to 2 tablespoons of baking soda mixed
with 1 quart of water, and then wipe dry. Repeat monthly.
• Blender gasket: After unplugging the blender, take all the pieces apart and either wash them in the dishwasher or clean them with warm, soapy water. Warn clients to
be careful not to cut themselves on the blade.
• Can opener: Place a dishwasher safe can opener in the dishwasher after each use. To hand wash, wash the can opener in hot soapy water, rinse thoroughly, and dry. Use
a stiff bristled brush to clean the food residue around the blade.
• Rubber spatula: If dishwasher safe, wash it in the dishwasher after every use. To hand wash, use warm soapy water and clean between the handle and the spatula head.
If it's a two-piece spatula, separate the handle from the spatula before cleaning.
• Food storage containers: If the lid and container are dishwasher safe, wash after every use. To wash by hand, use hot soapy water, making sure to clean the area
around the seal and any grooves where the cover attaches to the container. Rinse thoroughly and air dry.
Molds are fungi that are transported by air, water, or insects. Although they're visible with the naked eye, they have branches and roots that can grow deep into the food. Some molds can cause allergic reactions and respiratory issues. Under the right conditions, several types of mold can produce illness-causing toxins. Molds prefer warm temperatures; however, they easily can grow in your fridge. They like salty and sugary foods, including cured meats and jam.
Although the saying goes "when it doubt, throw it out," not all moldy foods need to be tossed. Hard cheeses and hard produce such as carrots, bell peppers, and cabbage don't have to be discarded. To remove the mold, cut off at least 1 inch around and below the mold spot. After cutting, use fresh wrap to cover it.
Yeast can spoil food quickly and result in food with an alcoholic smell or taste. The yeast may appear as a pink discoloration or slime. They tend to grow well in acidic foods such as jams, honey, and fruit. If a client suspects that a food contains yeast, the entire container should be discarded.
The following three main food safety practices can prevent all the illnesses described above. The tips provided below can be incorporated into education sessions with clients.
The transfer of microorganisms from one surface to the other easily can occur when using the same cutting board and surface to prepare raw and ready-to-eat food. It also can occur if raw meat is stored above ready-to-eat or cooked food in the refrigerator. To prevent cross-contamination, remind clients to wash cutting boards thoroughly with soap and water between handling raw meat and ready-to-eat food. They also can use two separate cutting boards. Synthetic cutting boards can be cleaned in a washing machine and should be changed if they become warped or have many cracks and crevices. When storing food in the refrigerator, raw meats should be placed on the bottom shelves, while ready-to-eat and cooked foods should be stored on top.
Foods that remain in the time-temperature danger zone between 41° F and 135° F for more than four hours can begin harboring pathogenic microorganisms. As a result, remind clients to refrigerate foods immediately when they get home from the market. Defrost foods in the refrigerator in advance and not on the countertop overnight. They also should cook foods until they reach their proper minimum internal cooking temperatures. Leftover foods shouldn't be kept at room temperature for more than two hours. Leftovers should be tossed after one hour when the temperature is 90° F or above.
Clients always should handle food with clean hands and perform proper hand washing. They also should wash their hands after using electronic devices (eg, cell phones, laptops, desktop computers, iPads, etc), using the restroom, and performing other tasks such as taking out the garbage. If the person preparing food is sick with symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, and sore throat with fever, they should avoid handling food until symptoms have resolved for at least 24 hours.
Food safety practices are used in many areas of dietetics. Below are three RDs in different areas of practice who incorporate food safety into their work.

We provide yoga services in all life style disorders and wellbeing
Heart conditions that include diseased vessels, structural problems and blood clots.
Read More
Diabetes - A group of diseases that result in too much sugar in the blood (high blood glucose).
Read More
Obesity - A disorder involving excessive body fat that increases the risk of health problems.
Read More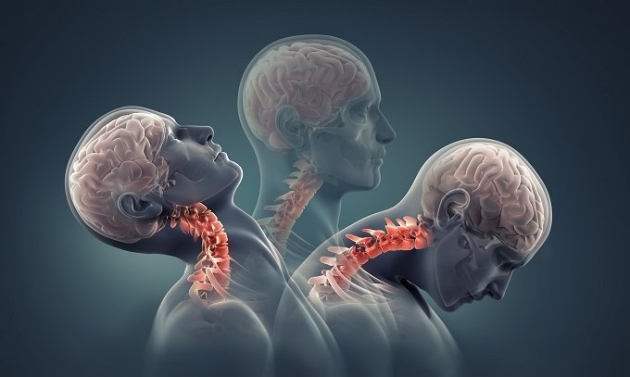
Cervical spondylosis is a common, age-related condition that affects the joints and discs in your cervical spine, which is in your neck.
Read More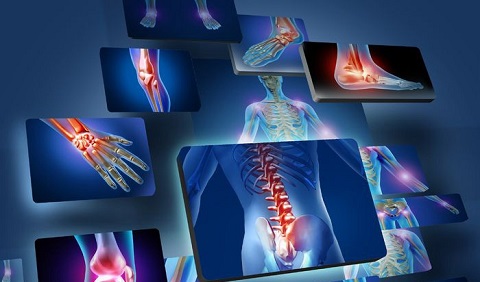
Arthritis - Inflammation of one or more joints, causing pain and stiffness that can worsen with age.
Read More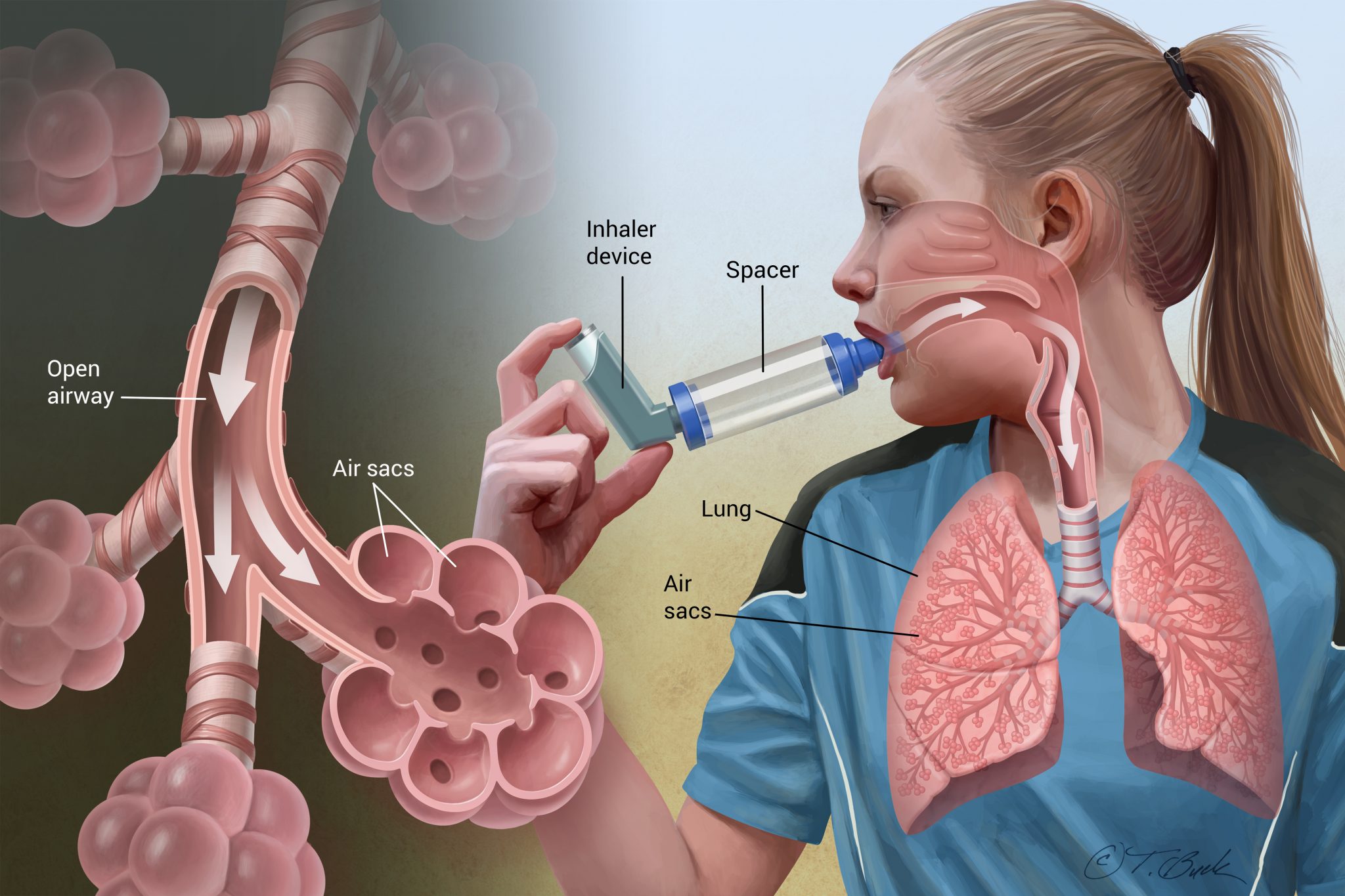
Asthma - A condition in which a person's airways become inflamed, narrow and swell and produce extra mucus, which makes it difficult to breathe.
Read More
A mental health disorder characterised by feelings of worry, anxiety or fear that are strong enough to interfere with one's daily activities.
Read More
PCOS - A hormonal disorder causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts on the outer edges.
Read More
Thyroid - Thyroid disease is a common problem that can cause symptoms because of over- or under-function of the thyroid gland.
Read More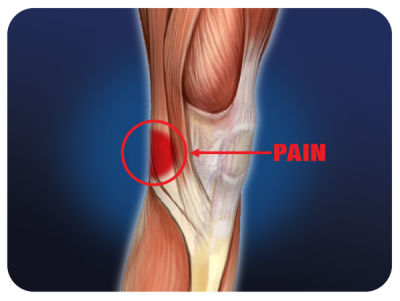
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative process that causes knee joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Read More
Migraine - A headache of varying intensity, often accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light and sound.
Read More
Gastric problems are usually more common in diabetics who have had the condition for longer, and is mostly caused by neuropathy affecting certain nerves in the digestive system.
Read More
Eye diseases like macular degeneration, glaucoma, and cataracts, can cause vision problems.
Read More
Shoulder problems happen when the soft tissues in the shoulder break down.
Read More
Yoga is for all age groups kids, children, tenage, young and adults.
Read More
Hair Loss - Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body.
Read More
Yoga helps to increase your height by opening your ligamnets, stiffed tendons, ball and socket joints.
Read More
Pranayama, breathing exercises, headstand, and fish pose are primarily the best for glowing skin.
Read More
Body Toning - Tone up you body curves and lose weight by yoga asanas.
Read More
General Fitness by yoga includes physical, mental and spiritual wellbeing.
Read More